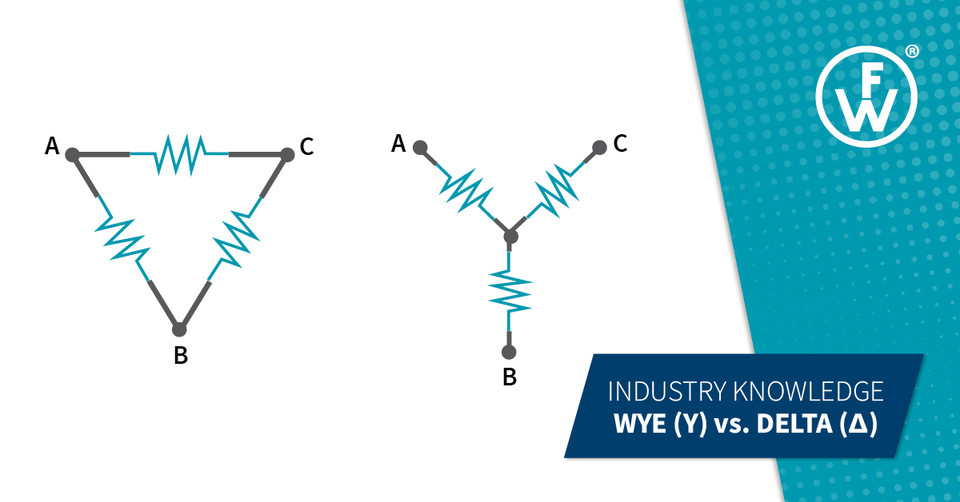
If you work with industrial power, you’ve heard the terms: Wye and Delta. They’re two ways of wiring a 3-phase electrical system — and while they deliver the same type of power, they do it differently, with real implications for voltage, equipment compatibility, and safety.
Whether you're sizing up a new power source, specifying a portable power distribution unit (PDU), or selecting the right plug and connector, understanding the difference matters. Here's what to know — and when to care.
The Basics: Wye vs. Delta
Both Wye (Y) and Delta (Δ) are 3-phase power configurations used to distribute electrical loads efficiently. What separates them is how the circuit is wired:
Wye Configuration
- Also called “star”
- 3 hot wires + 1 neutral
- Neutral allows line-to-neutral connections (single-phase loads)
- Common in buildings, utilities, and commercial distribution
- Offers multiple voltage levels — e.g., 120/208V or 277/480V
Delta Configuration
- 3 hot wires with no neutral (typically)
- All loads are line-to-line
- Often used in heavy industrial or motor-heavy environments
- Delivers consistent voltage across all three lines — e.g., 240V, 480V
Why It Matters in Real-World Applications
Knowing your power configuration helps you:
- Select compatible equipment (especially if voltage changes are involved)
- Design for grounding and protection properly
- Choose the right connectors or distribution gear
You can’t plug a 208V-rated piece of equipment into a 480V source and expect it to work — or survive. And in portable applications, like generator-fed PDUs or temporary power drops, mismatches are easy to make without the right safeguards in place.
Where IEC Pin & Sleeve Devices Come In
This is where standardized industrial connectors earn their keep. Walther’s IEC 60309 Pin & Sleeve devices are designed to eliminate human error when dealing with different voltages — including Wye and Delta systems.
Here’s what’s useful to know:
- Each device is keyed by a ground pin position, using a clock-based coding system developed by Walther-Werke in alignment with IEC 60309-1 and 60309-2
- Mismatched voltages can't be connected — devices physically won’t mate if the configuration is incorrect
- Wye and Delta configurations are keyed differently, preventing cross-connection
For example, a 3ØY 277/480V device (like the 100A plug 279519) won’t fit with a 3Ø 480V Delta device (like the 100A connector 279419).
That level of safety is baked into the IEC standard — which is why these connectors are trusted worldwide in high-risk or high-traffic electrical environments. Whether your 3-phase power source is Wye or Delta, IEC devices help ensure you're plugging into the right voltage — safely and consistently.
When You Need to Know the Difference
Most electrical professionals don’t need to memorize transformer theory. But knowing whether your site uses Wye or Delta power helps with:
- Selecting the right distribution equipment
- Sourcing compatible connectors or adapters
- Determining grounding requirements
- Working safely with or around energized systems
In other words: If you’re supplying or tapping into 3-phase power, knowing your system type isn’t just useful — it’s essential.
The Bottom Line
Wye and Delta are two sides of the same 3-phase coin. But they behave differently — and knowing the difference helps you plan smarter, protect equipment, and avoid costly mismatches.
If you're working with temporary power, permanent distribution, or IEC-rated connectors, understanding your source configuration is the first step.
Learn more in our IEC Pin & Sleeve catalog
Or explore Walther’s full line of power distribution solutions built for your environment.
View Catalog: IEC 60309 Pin & Sleeve Devices (Full Catalog)
Shop Products: Pin & Sleeve Devices